ARMD Full Form | What is Age Related Macular Degeneration
What is the full form of ARMD
ARMD: Age Related Macular Degeneration
ARMD stands for Age Related Macular Degeneration. It is a common eye condition among people over the age of 60, more likely to develop as a person ages. It affects the central part of the retina, called macula. It gradually deteriorates macula which results in blurred or reduced central vision. The macula is responsible for clear vision in your direct line of sight (central vision). So, it causes changes in your central vision and makes everyday tasks difficult.
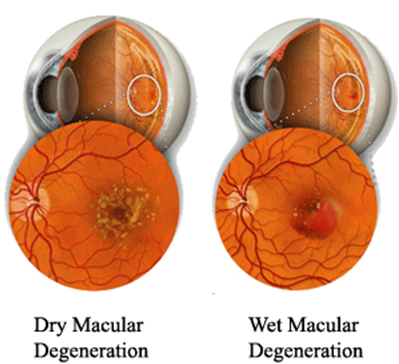
Types of AMD
AMD is of two types: Dry AMD and Wet AMD
Dry AMD: It is the most common type of AMD, characterized by the occurrence of yellow deposits (drusen) in the macula. It progresses slowly, so causes a gradual change in your central vision. In the advanced stages, it may cause a blank patch or blind spot in the centre of a person's vision.
Dry AMD:WET AMD: It is a less common form of macular generation which progresses quickly and causes severe changes in a person?s central vision in a short period of time, over few days or weeks. It causes the growth of new abnormal blood vessels from choroid, a layer underneath the macula. This change is known as choroidal neovascularization. These vessels may leak blood and fluid under the macula which results in scarring of the macula and thus causes distortion of central vision and may lead to permanent loss of central vision.
WET AMD:Risk Factors:
- Aging
- Genetic
- Smoking
- Cardiovascular disease
- Hypertension
- Deficiency of omega-3 fatty acids
- Low intake of green leafy vegetables
Symptoms:
- Visuals distortions
- Reduced central vision
- Sentences on a page appear wavy or distorted
- Blurred vision
- Blurry areas on a printed page
- Decreased intensity or brightness of colors
- Difficulty in recognizing faces
Its diagnosis involves:
- Visual acuity test
- Dilated eye exam
- Amsler grid
- Funduscopic examination
- Color fundus photography
- Optical coherence tomography
- Fluorescein angiography