GIS Full Form | What is Geographic Information System
What is the full form of GIS
GIS: Geographic Information System
GIS stands for Geographic Information System. It is a system designed to collect, analyze, manipulate, manage, and display all types of geographical and spatial data and information. It allows you to perform spatial analysis and manage large data and display the information in maps or graphical form for analysis and presentation. These benefits make GIS a valuable tool to visualize spatial data or to build decision support systems for an organization.
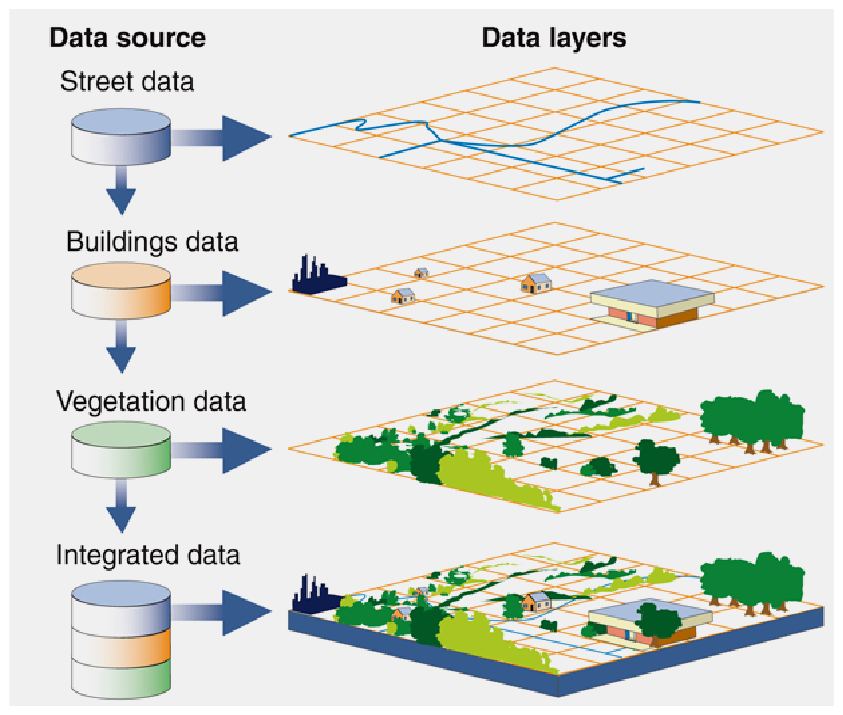
A GIS stores data on geographical features and their characteristics. These features are known as points, lines, areas, or raster images. For example, in the map of a city, road data can be stored as lines, and boundaries can be stored as areas, and aerial photos can be stored as raster images.
GIS store information using spatial indices that allows identifying the features located in any arbitrary region on a map. For example, a GIS can quickly identify and map all of the locations within a specified radius of a point, or all of the streets or roads that pass through a territory.
Some data can be spatial (locations on the earth), coupled with tabular data (attribute data). Attribute data generally refers to additional information about each of the spatial features. For example, the actual location of the hospitals in a geographical area is spatial data. Additional data such as hospital name, level of treatment, and bed capacity are the attribute data. So, GIS is a combination of these two data types that makes it an effective problem-solving tool through spatial analysis.
GIS not only tells the location of features but also provides additional information related to a feature such as:
- Relationship of a feature with other features
- Where the most or least of a feature exists
- The density of features in a specific space
- What is happening inside an area of interest (AOI)
- What is happening nearby some features
- How an area has changed over the years
For example, a rare species of a plant is found in three different places, and spatial analysis shows that the plants are only on the south-facing slopes above an elevation of 1,500 feet and get more than fifteen inches of rain per year. So, with the help of GIS maps, we can display all locations in the area that have similar conditions and can look for this plant species. Similarly, we can find out the locations of farms that are using a specific fertilizer, and the location of streams and rainfall to find out which streams may carry the fertilizer downstream.