MAC Full Form | What is Media Access Control Address
What is the full form of MAC
MAC: Media Access Control Address
MAC stands for Media Access Control Address. It is a hardware identification number that identifies each device connected to a network. The MAC address is embedded into network interface cards (NIC) in your computer such as an Ethernet card or Wi-Fi card, at time of manufacturing by the vendor, so it cannot be changed. So, it is a hardware number of a computer, which is also known as a physical address or a hardware address of a network device.
The Network Interface Card (NIC) is a computer circuit card that enables your computer to connect to a network. It converts the data into an electrical signal that can be transmitted over the network. So, in a network, along with an IP address, there is also a hardware address. IP addresses are related to TCP/IP, whereas MAC addresses are associated with the hardware of network adapters. So, MAC is a computer's unique hardware number, i.e., a unique identifier for an Ethernet or network adapter over a network.
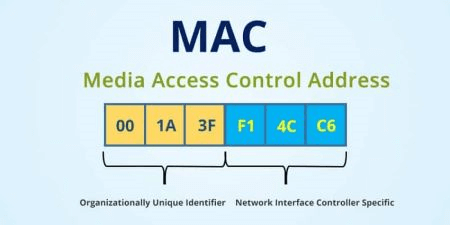
There are plenty of networkable devices, and each is required to have a unique MAC address, so there must be many addresses. Accordingly, MAC addresses comprise of six two-digit hexadecimal numbers separated by colons. For example, an Ethernet card can have a MAC address of 0d:00:b1:8e:83:C1. So, it is a 12 digit hexadecimal number, which is a 6-byte binary number and is represented by Colon-Hexadecimal notation.
First 6 digits of MAC address provides information about the manufacturer; it is called OUI (Organizational Unique Identifier). The next or last 6 digits identify the Network Interface Controller, which is assigned by the manufacturer. The network automatically recognizes this number, and we don't need to remember the address. IEEE Registration Authority Committee assigns the MAC prefixes to its registered vendors.
OUI of some famous manufacturers:
- 3C:5A:B4: Google, Inc.
- CC: 46: D6: Cisco
- 3C:D9:2B: Hewlett Packard