OCR Full Form | What is Optical Character Recognition
What is the full form of OCR
OCR: Optical Character Recognition
OCR stands for optical character recognition. It is also known as an optical character reader (OCR) or text recognition. It is designed to convert scanned paper documents, or images of documents captured by a digital camera into readable, editable and searchable data.
The scanned page of a physical document can be displayed on the screen and can be read, but for the computer, it is just a series of black and white dots, which it cannot recognise. To enable the computer to read a scanned document and produce a soft copy, OCR was developed. OCR examines the text of a scanned document and translates the characters into code that makes the text machine-readable so that it can be transformed into an electronic format or soft copy just like a document created with a word processor which users can edit, format, search and read.
Thus, it helps computer recognize words and characters on a scanned page or digital images of physical printed or handwritten documents by using the optical properties of words and characters printed on a scanned page or document.
An OCR device is made up of hardware and software combination, designed to convert physical documents into machine-readable text. Hardware of OCR (optical scanner or a circuit board) copies and reads the text, whereas the software deals with the advanced processing. The software can also make use of artificial intelligence to use advanced methods of intelligent character recognition (ICR), like the ability to identify language or style of handwriting.
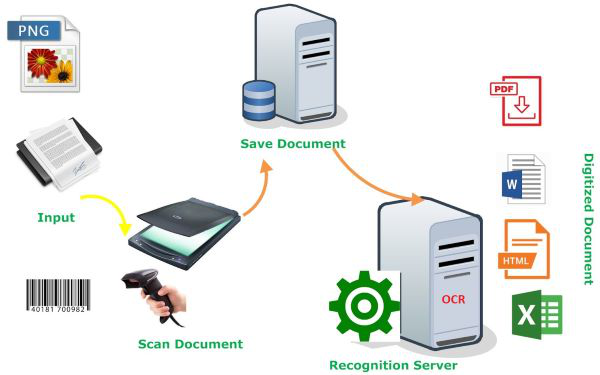
How OCR works:
- The scanner processes the physical form of the document.
- Once the document is scanned, the software analyses its structure and converts it into a coloured (black and white) version.
- The scanned document is examined for light and dark areas.
- The dark areas are identified as characters, and light areas are identified as background.
- The dark areas are further analysed to identify letters or numeric digits. The lines are divided into words and words into characters. OCR attempts to determine if the dark areas represent a particular letter or number.
- Once the characters are singled out and identified, they are converted into an ASCII code that can be used by computer systems to handle further manipulations and thereby presents you the recognized text.
OCR software may vary in their techniques, but generally analyse one character, word or block of text at a time and then identify characters using one of the following two algorithms.
1) Pattern recognition: OCR software are developed by feeding the examples of text with different fonts and formats, so they understand the shape or pattern of characters and accordingly identify them correctly.
Pattern recognition2) Feature detection: In this technique, the OCR programs rely on the feature of a character or a number. The features may include the number of angled lines, crossed lines, or curves in a character. For example, the letter 'A' may be stored as two lines connected to a horizontal line at the middle and also joined together at one end.
Feature detection