DHCP Full Form | What is Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
What is the full form of DHCP
DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
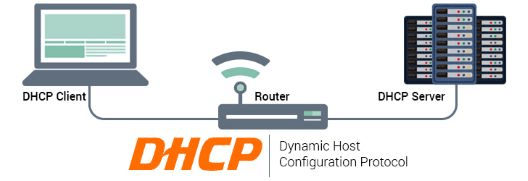
DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). It is also known as RFC 2131. It is a network protocol that allows a server to automatically assign an IP address from a specified range of numbers (a scope) to a computer or device when it is connected to a given network. So, it is a protocol for assigning dynamic IP addresses to devices on a network. DHCP automatically permits a node or device to be configured automatically, so a network administrator is not required.
What Does DHCP Do?
- It controls the establishment of all the devices added to the network or dropped from the network.
- It maintains the IP address of the host through a DHCP server.
- It informs the DHCP server when a node or client, which is configured to work with DHCP, is added to the network. The server responds by providing an IP address to the client/node.
How DHCP Works?
In small businesses or small networks, the router acts as a DHCP server. Whereas, in large networks, a single computer may act as the DHCP server. In simple words, a device or client requests an IP address from the router or host, which assigns an IP address available at that moment to the client to enable it to communicate on the network.
So, when a device is connected to a DHCP server, it sends a request to the server, called a DHCPDISCOVER request. After receiving the request, the server finds an IP address for the device and offers it to the client with a DHCPOFFER packet.
After receiving the offer, the device responds to the DHCP server with a DHCPREQUEST packet to show that it agrees to accept it. After that, the server confirms by sending an ACK (acknowledgement) that this IP address has been provided to this device and also specifies the duration for which the device can use the address before getting a new IP address. If the server cannot provide or does not have an IP address for the device, it will send a NACK (negative acknowledgement).