DHT Full Form | What is Dihydrotestosterone
What is the full form of DHT
DHT: Dihydrotestosterone
DHT stands for Dihydrotestosterone or 5?-dihydrotestosterone (5?-DHT). It is also known as androstanolone or stanolone. It is a sex hormone that stimulates the development of male characteristics. It is produced in the body of both men and women, but utilized more by men than women. DHT is produced when an androgen, male sex hormone usually testosterone, is metabolized by an enzyme called 5aR (5 alpha reductase). DHT is responsible for regulating neurological health, blood cell formation and some physiological changes like Alopecia.
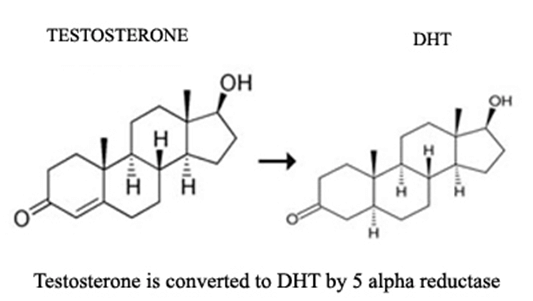
DHT is also associated with baldness. Let us see, how it causes baldness:
DHT receptors are located throughout our body, mainly in the hair follicles. In some people, the hair follicles are very sensitive to DHT due to their genetic makeup. In such people, if the amount of DHT increases in the body, it can block the dermal papilla within the hair follicle. Dermal papilla supplies nutrients to the hair bulb from where the new hair originates. So, if the dermal papilla gets blocked due to DHT, the hair bulb will not get the sufficient nutrients to produce new hair. The hair follicle itself also tends to shrink due to the DHT. It does not cause hair to fall out rather it affects the follicles' ability to produce new hair.
There are certain medications that can help stimulate hair growth by preventing the 5aR enzyme from converting the testosterone into Dihydrotestosterone. This brings down the levels of DHT in our body and thus reduces its detrimental effects on hair follicles. These medications are known as 5 Alpha-Reductase inhibitors.
DHT is also associated with prostate cancer. It causes the prostate to develop and keeps stimulating the prostate to grow. The cells of the prostate continue to multiply and the risk of mutation increases with age. These mutations may cause Benign Prostate Hyperplasia, a precursor of prostate cancer.