DSL Full Form | What is Digital Subscriber Line
What is the full form of DSL
DSL: Digital Subscriber Line
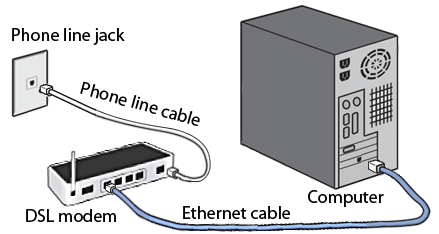
DSL stands for Digital Subscriber Line. DSL is a communication medium used to transfer high speed internet over standard copper wire telecommunication line. DSL offers the best cost, connectivity and services over other internet access types like broadband.
Data transfer and telephone conversation can be done simultaneously over a DSL. Over the 'voiceband' frequency range, voice signal is transmitted using low frequencies (0Hz to 4kHz). While digital signals are transmitted through high frequencies (25kHz to 1.5MHz). To make sure that phone call does not get interrupted by high frequencies, DSL filters or splitters are used.
Types of DSL
- SDSL:Symmetric DSL provides equal bandwidth for both uploading and downloading and is mostly preferred by small organizations.
- ADSL:Asymmetric DSL. Most users download more data then they upload, for this they use ADL. In this, downstream speed is much more than upstream. Uploading capacity may not work as good as downloading capacity. Users who do not upload that much in comparison to downloading can use ASDL. It may offer as high as 20 Mbps speed for downloading while for uploading 1.5 Mbps.
- HDSL: It is high bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line. It is a wideband digital transmission which is used within a corporate site and between the telephone company and its customers. It is a symmetrical line, offers equal bandwidth in both directions.
- RADSL: It is Rate-Adaptive DSL. In this DSL technology, the modem is capable of adjusting bandwidth and operating speed to maximize the data transfer. It supports both symmetrical and asymmetrical applications with variable speeds.
- VDSL: It is very high data rate DSL. It is a developing DSL technology that offers more reliable internet experience than basic broadband. It offers much higher data transfer rate over short distances, e.g. 50 to 55 Mbps over lines up to 300 meters in length.
Features
- It is widely available.
- It is less costly, offers more security.
- It is much reliable than other broadband service.
- It offers less speed than broadband service.
- It provides a limited range due to which internet quality is affected due to larger distance between main hub DSL provider and receiver.