TB Full Form | What is Tuberculosis
What is the full form of TB?
TB: Tuberculosis
TB stands for Tuberculosis. It is an infectious disease that is caused by a bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which is an aerobic bacteria that grows slowly and can grow within body cells. It mostly affects the lungs of a person. TB is curable, however, if proper treatment is not being taken by the patient, it may cause death.
Mycobacterium tuberculosisMycobacterium tuberculosismostly affects the lungsmostly affects the lungs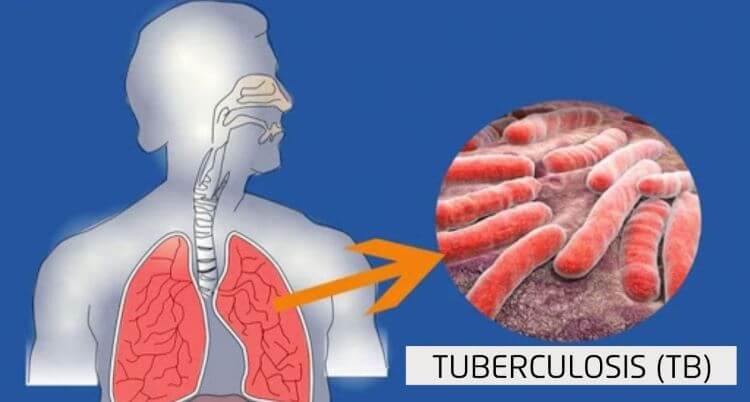
It is a highly contagious disease as it spreads from person to person. For example, when a TB patient sneezes or coughs, the TB germs are released into the air. When a healthy person inhales these germs he or she gets infected. It is diagnosed by a skin test which if comes positive is followed by an X-ray of the chest that is done to find out the status of the infection.
Types of TB
There are two major types of TB:
two major types of TBtwo major types of TBLatent TB: In this type of TB, the infected person has germs in their body but they are not ill and don't transmit disease. Also, they don't show symptoms of TB. Around 1/3 population of the world is infected with latent TB which means although they are infected, they are not ill yet and cannot transmit the disease. People who have a weak immune system, suffering from malnutrition or other diseases like diabetes or using tobacco are at a higher risk of getting infected with TB or to progress from latent to active TB.
Latent TBActive TB: This is the severe type of TB in which the germs multiply and cause illness and symptoms of TB. A person with active TB can spread TB to other healthy persons.
Active TBSome of the common symptoms of TB are as follows:
common symptoms of TBcommon symptoms of TB- Cough that continues more than two or three weeks
- Pain in the chest
- Coughing up blood
- Loss of appetite
- Unintentional Weight loss
- Fever, chills and night sweats
- Pain in the bones
Treatment of TB:
The treatment of TB is a lengthy process in which the patient is required to take medication regularly without any gap. For the cure of TB, the World Health Organization (WHO) introduced a plan to control TB. This plan is known as 'Directly observed treatment, short course' (DOTS). As per this strategy, a nurse or any other health care worker prescribes the TB drugs to patients and makes sure the patient takes medicine regularly and complete the course.
Directly observed treatment, short course' (DOTS)Directly observed treatment, short course' (DOTS)A TB patient may take the following precautions to prevent the spread of TB:
- Cover mouth with a tissue while sneezing or coughing. Seal the tissue in a plastic bag before throwing it away or putting in the dustbin
- Wash hands properly after sneezing or coughing
- Stay at home, avoid going to work, school, markets or other public places
- Don't visit other people as well as don't invite anyone to visit you
- Avoid public transportation
- Wear a mask while going out for the work that cannot be avoided